Audit Logging Specifics
While the Keyfactor Command audit log functionality covers the entire product, the following areas may be of particular interest.
When a user tries to access a page in the Management Portal or an API![]() A set of functions to allow creation of applications. Keyfactor offers the Keyfactor API, which allows third-party software to integrate with the advanced certificate enrollment and management features of Keyfactor Command. endpoint
A set of functions to allow creation of applications. Keyfactor offers the Keyfactor API, which allows third-party software to integrate with the advanced certificate enrollment and management features of Keyfactor Command. endpoint![]() An endpoint is a URL that enables the API to gain access to resources on a server. that they don’t have access to, they will receive an error and a warning will be logged in the audit log.
An endpoint is a URL that enables the API to gain access to resources on a server. that they don’t have access to, they will receive an error and a warning will be logged in the audit log.

Figure 380: Management Portal Access Denied Message
The audit log shows the level as Warning and the category as Authorization Failure with a message detailing the user and the requested page.
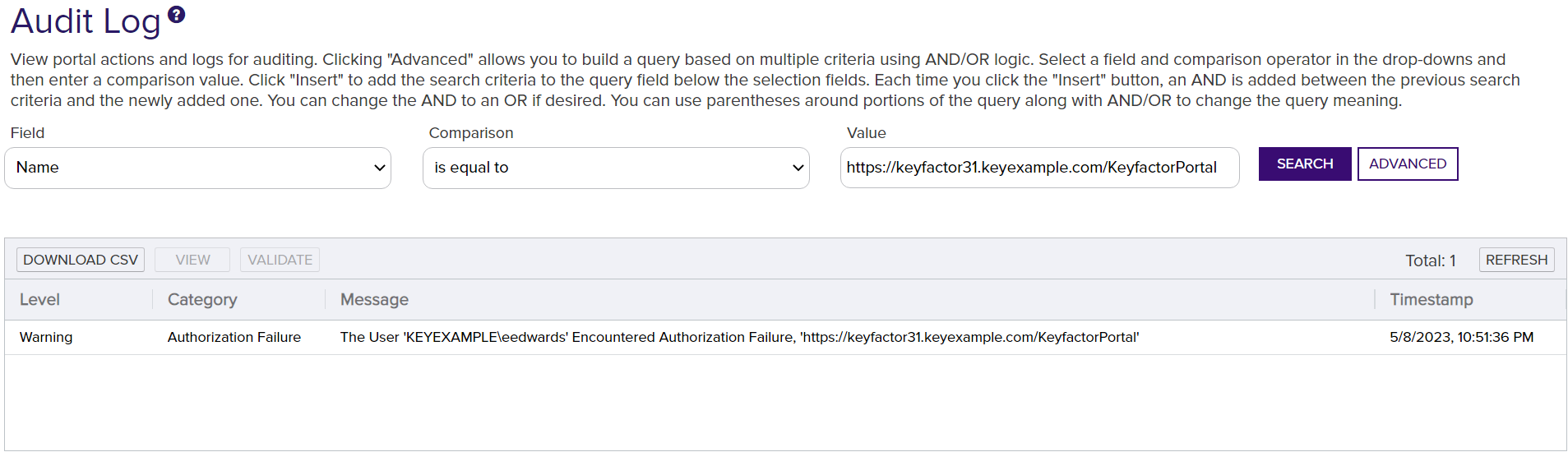
Figure 381: Audit Log Authorization Failure Messages
Click View to see the details dialog:
- Username
The user making the page request. - Request Route
The page the user requested. - Request Type
Either API Endpoint or Portal Page. - HTTP Verb
This appears for both API requests and portal requests. For API requests, this can help to determine which action was denied. - User's Roles
The security role or roles that the user holds (see Security Roles and Claims). A role will not be listed if the user denied access is not a user in Keyfactor Command.
For more information about the audit log details, see View: Audit Log Details.
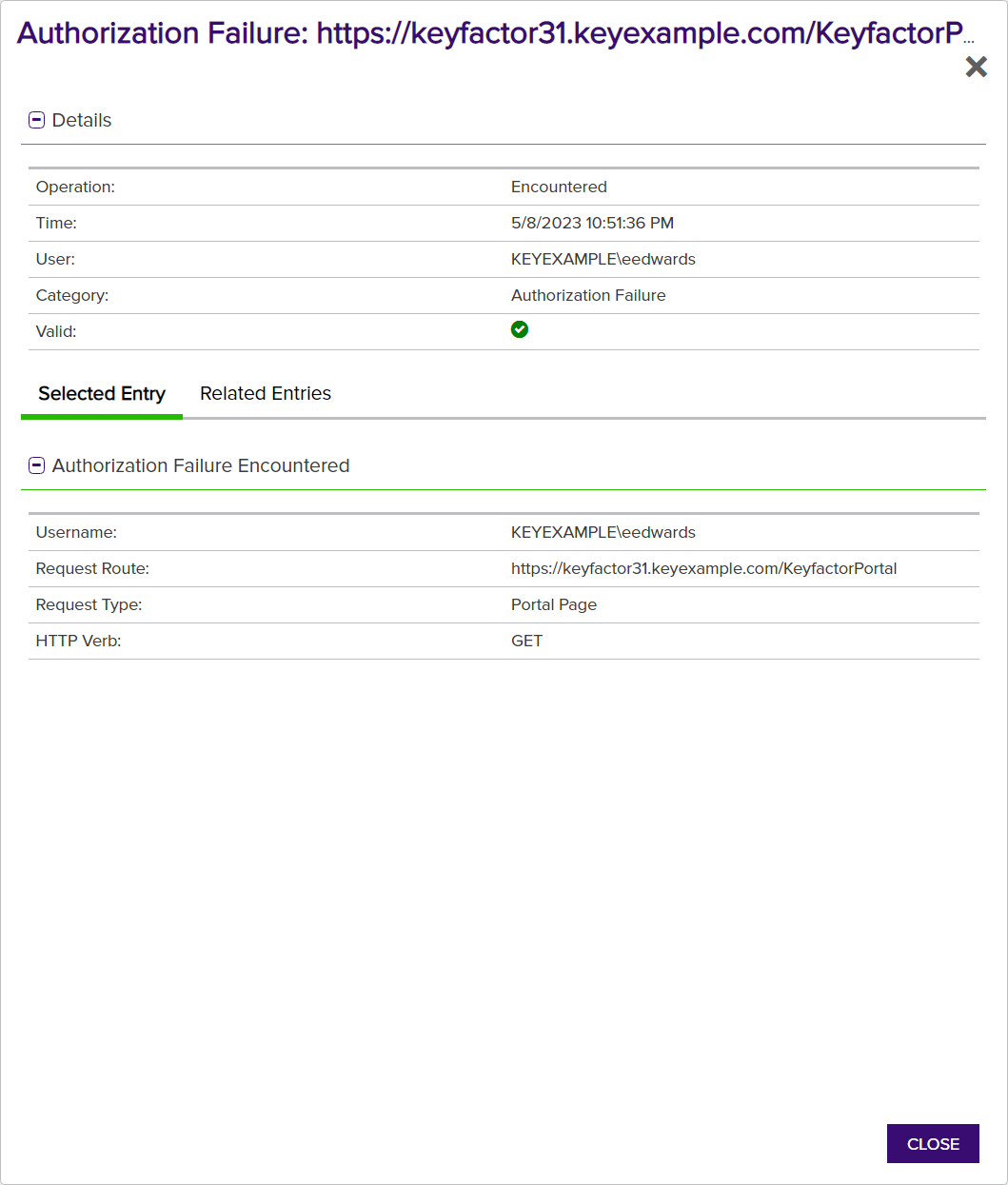
Figure 382: Authorization Failure Audit Log Detail
Tracking of operations related to certificates is especially extensive. Certificate-related operations that are audited include:
- Certificate revocation (Category: Certificate)
- Certificate download (Category: Certificate)
- Enrollment
 Certificate enrollment refers to the process by which a user requests a digital certificate. The user must submit the request to a certificate authority (CA). for certificates via PFX
Certificate enrollment refers to the process by which a user requests a digital certificate. The user must submit the request to a certificate authority (CA). for certificates via PFX A PFX file (personal information exchange format), also known as a PKCS#12 archive, is a single, password-protected certificate archive that contains both the public and matching private key and, optionally, the certificate chain. It is a common format for Windows servers. enrollment and CSR
A PFX file (personal information exchange format), also known as a PKCS#12 archive, is a single, password-protected certificate archive that contains both the public and matching private key and, optionally, the certificate chain. It is a common format for Windows servers. enrollment and CSR A CSR or certificate signing request is a block of encoded text that is submitted to a CA when enrolling for a certificate. When you generate a CSR within Keyfactor Command, the matching private key for it is stored in Keyfactor Command in encrypted format and will be married with the certificate once returned from the CA. enrollment (Category: Certificate)
A CSR or certificate signing request is a block of encoded text that is submitted to a CA when enrolling for a certificate. When you generate a CSR within Keyfactor Command, the matching private key for it is stored in Keyfactor Command in encrypted format and will be married with the certificate once returned from the CA. enrollment (Category: Certificate) - Certificate renewal via one-click or seeded renewal (Category: Certificate)
- CSR generation, re-download and deletion (Category: CSR)
- Approval of certificate requests made using templates requiring manager approval at the CA
 A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. level (Category: Certificate Request—see also Workflow)
A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. level (Category: Certificate Request—see also Workflow) - Certificate deletion (Category: Certificate)
- Certificate metadata
 Metadata provides information about a piece of data. It is used to summarize basic information about data, which can make working with the data easier. In the context of Keyfactor Command, the certificate metadata feature allows you to create custom metadata fields that allow you to tag certificates with tracking information about certificates. operations—addition of or updates to metadata tags on certificates (Category: Certificate)
Metadata provides information about a piece of data. It is used to summarize basic information about data, which can make working with the data easier. In the context of Keyfactor Command, the certificate metadata feature allows you to create custom metadata fields that allow you to tag certificates with tracking information about certificates. operations—addition of or updates to metadata tags on certificates (Category: Certificate) - Certificate collection
 The certificate search function allows you to query the Keyfactor Command database for certificates from any available source based on any criteria of the certificates and save the results as a collection that will be availble in other places in the Management Portal (e.g. expiration alerts and certain reports). creation or modification (Category: Certificate)
The certificate search function allows you to query the Keyfactor Command database for certificates from any available source based on any criteria of the certificates and save the results as a collection that will be availble in other places in the Management Portal (e.g. expiration alerts and certain reports). creation or modification (Category: Certificate) - Addition of certificates to and removal from certificate stores (Category: Certificate Store)
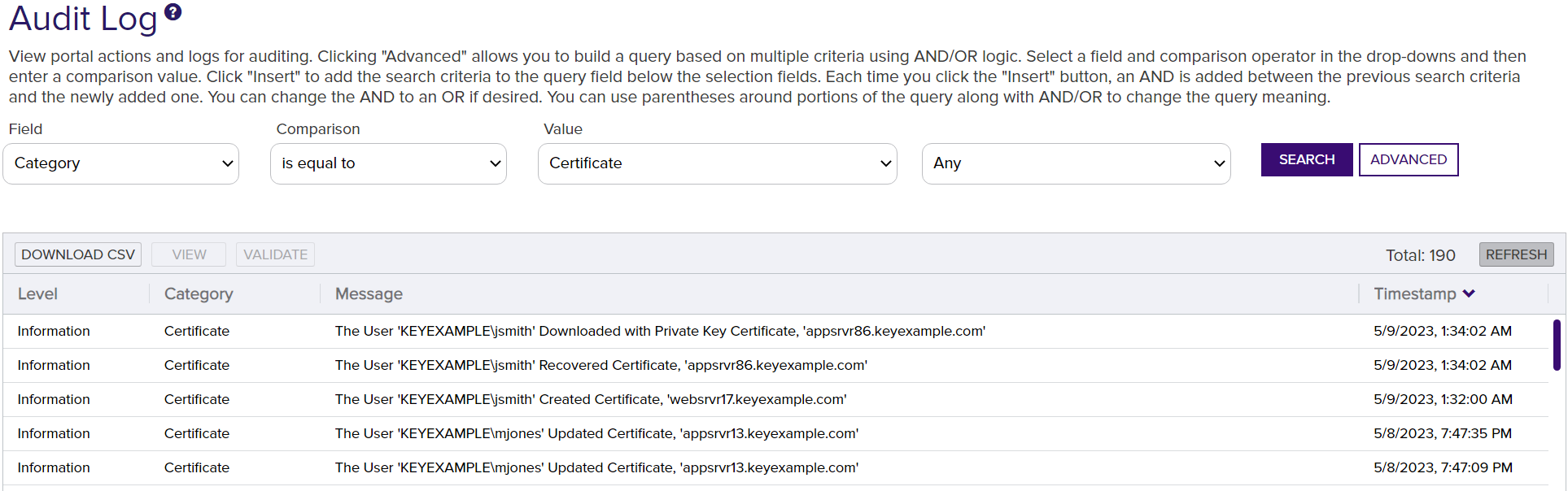
Figure 383: Audit Logs for Certificates
The management of security identities and roles to limit access to the Keyfactor Command Management Portal and Keyfactor API generates audit log entries as roles and identities are created, updated, and deleted. This includes the granting of permissions to roles and the assigning of roles to identities (these are considered updates). The Security Identity and Security Role categories do not cover any attempts to access the system. These are tracked separately using the Authorization Failure category (see Access Control). Successful authorizations are not logged.
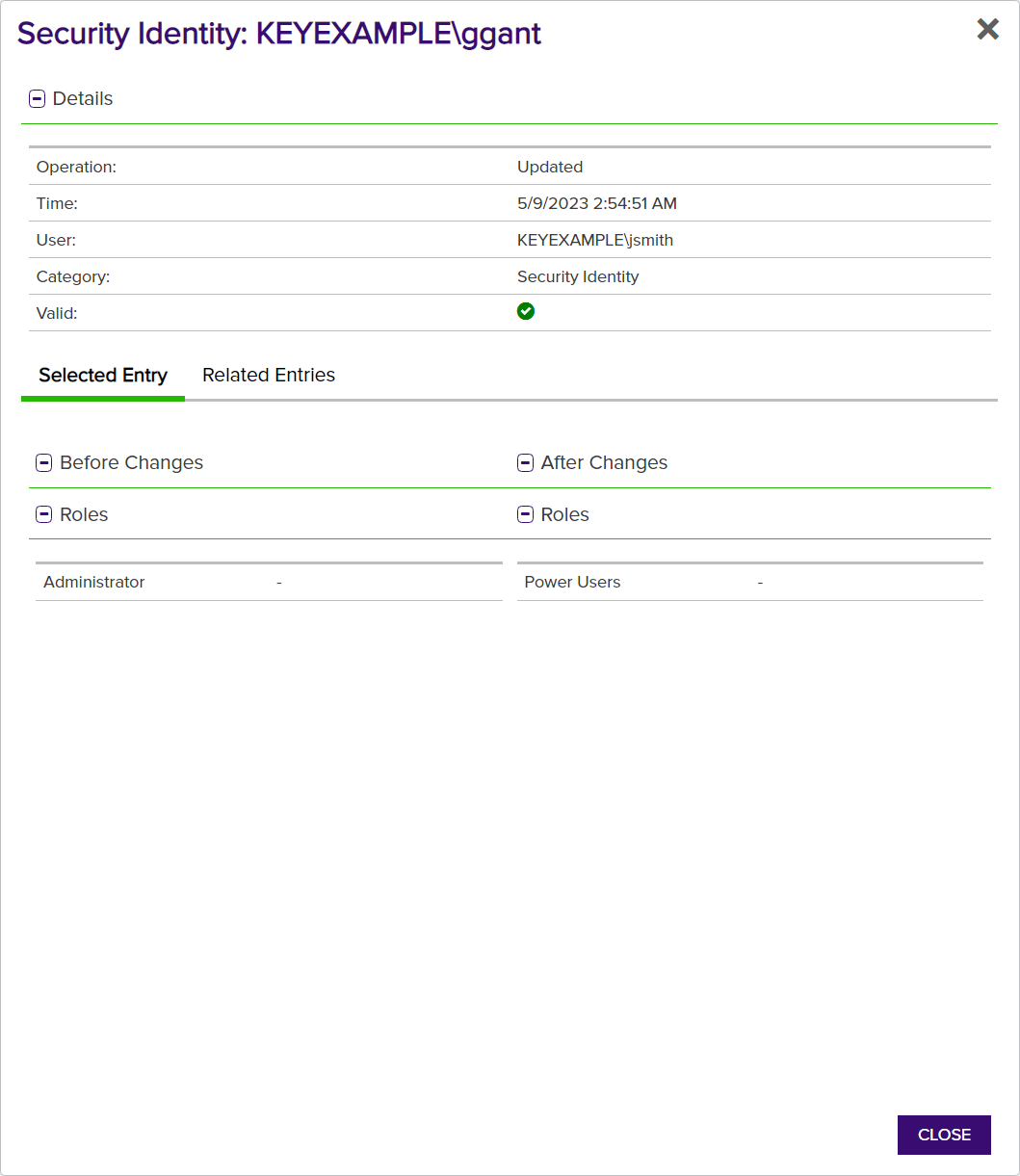
Figure 384: Audit Log Details for Security
SSH![]() The SSH (secure shell) protocol provides for secure connections between computers. It provides several options for authentication, including public key, and protects the communications with strong encryption. key management with the Keyfactor Bash Orchestrator
The SSH (secure shell) protocol provides for secure connections between computers. It provides several options for authentication, including public key, and protects the communications with strong encryption. key management with the Keyfactor Bash Orchestrator![]() The Bash Orchestrator, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to discover and manage SSH keys across an enterprise. generates a wide variety of audit log entries, including:
The Bash Orchestrator, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to discover and manage SSH keys across an enterprise. generates a wide variety of audit log entries, including:
-
An SSH user key is created or updated (with an object name of the user)
-
An SSH service account key is created, updated, or deleted (with an object name of the service account)
-
An SSH key is updated or deleted (with an object name of the public key
 In asymmetric cryptography, public keys are used together in a key pair with a private key. The private key is retained by the key's creator while the public key is widely distributed to any user or target needing to interact with the holder of the private key. fingerprint rather than user or service account name—this references the same key as issued for the user or service account)
In asymmetric cryptography, public keys are used together in a key pair with a private key. The private key is retained by the key's creator while the public key is widely distributed to any user or target needing to interact with the holder of the private key. fingerprint rather than user or service account name—this references the same key as issued for the user or service account) -
An SSH logon is created, updated, or deleted
-
An SSH server is created, updated, or deleted
-
An SSH server group is created, updated, or deleted
-
A rogue SSH key is identified associated with a logon while scanning a server configured for SSH key management
-
An SSH key rotation alert is created, updated or deleted
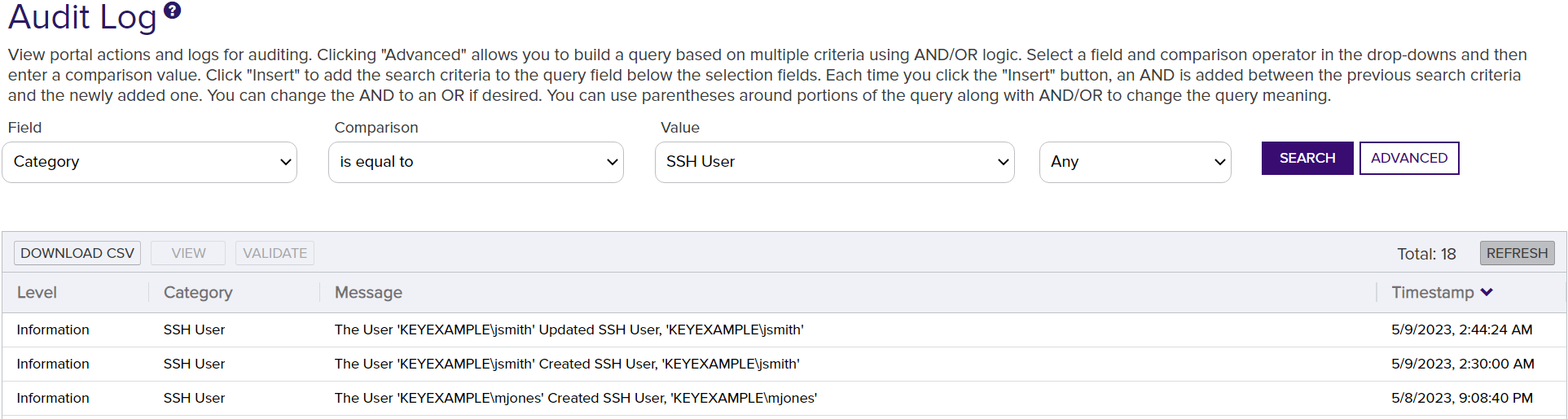
Figure 385: Audit Logs for SSH Management
Audit log entries are created during the initial Keyfactor Command installation process when the initial templates and API applications are configured and application settings established. Audit log entries may also be created when you re-run the Keyfactor Command configuration wizard if you make an auditable change in the wizard. When you upgrade from a previous version of Keyfactor Command or make a change in the configuration wizard to an existing Keyfactor Command installation, the audit log entries will show as Updated. The exact number of entries created depends on the configuration options selected, number of templates, and the templates configured for enrollment in Keyfactor Command.
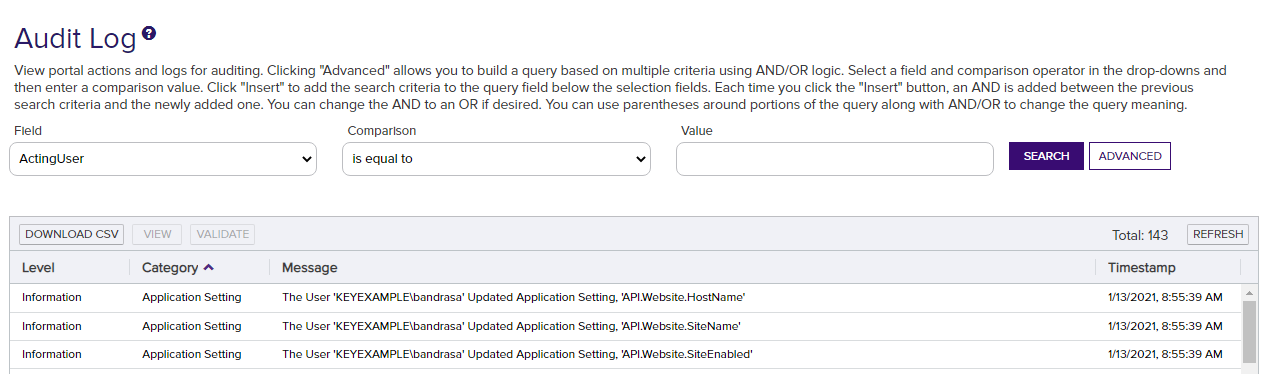
Figure 386: Automated Entries Created by the System in the Audit Log
Audit log entries that are generated for workflow include:
-
Workflow definition is created
-
Workflow definition is imported
-
Workflow definition is edited and saved
-
Workflow definition is published
-
Workflow definition is deleted
-
Workflow instance is initiated (created)
-
Workflow instance is suspended due to workflow configuration (e.g. the workflow requires approval)
-
Workflow instance is stopped manually (this appears as an update to the status of the workflow from Can Receive Signals = True to Can Receive Signals = False)
-
Workflow instance is restarted
-
Workflow instance failed
-
Workflow instance completed
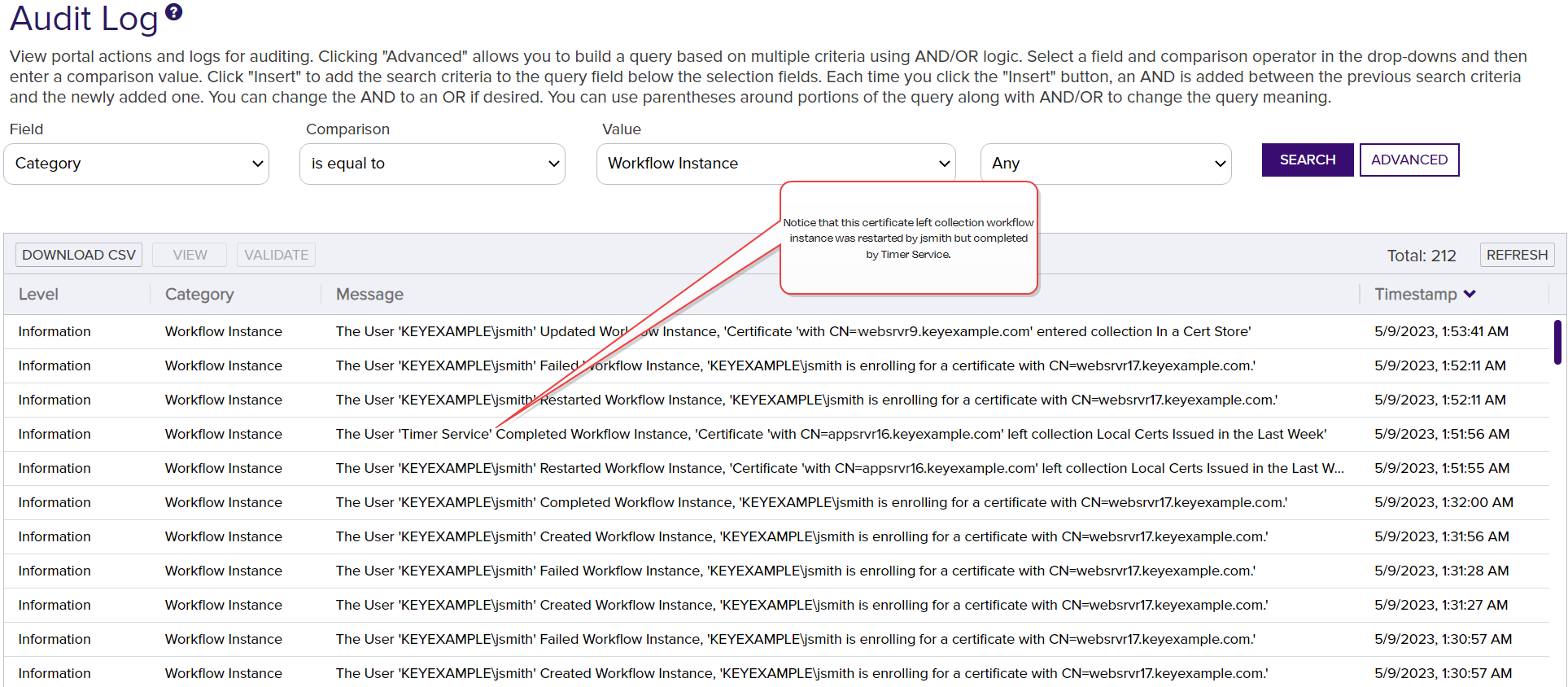
Figure 387: Audit Log Entries for Workflow
For more information about the audit log and using the audit log search feature, see Audit Log.